In many areas, digitalization can make a significant contribution to saving energy and thus reducing CO2 emissions through the intelligent control of devices, systems, processes and networks. The other side of the coin is that the production and operation of electronic devices requires a high level of resources and energy consumption. Fraunhofer EMFT is working on optimization approaches and innovative technologies for information and communication technology designed to protect the environment and save resources. The entire life cycle of microelectronic components is taken into account. A large part of the research activities are embedded in the Green ICT initiative funded by the BMBF.
Resource efficiency in microelectronics
The production of microelectronics still requires a high input of energy and resources. In addition, some processes use critical or environmentally harmful materials. As part of its Green ICT research activities, Fraunhofer EMFT is working on optimizing lithography and etching processes with the aim of reducing chemical and energy consumption. The use of new materials to replace critical or environmentally harmful chemicals is also being tested, for example in solvents or cleaning gases. In addition, Fraunhofer EMFT's abatement facility demonstrates how harmful emissions from the cleanroom into the environment, e.g. from noxious gases and toxic or corrosive substances from the installed equipment, can be significantly reduced.
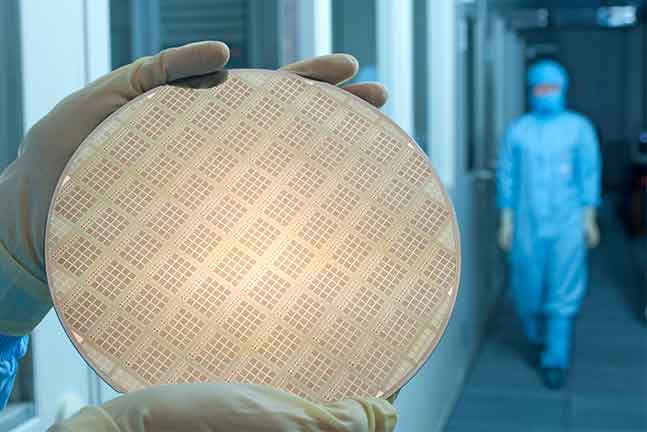


As sensors, electronics and artificial intelligence (AI) become more prevalent in an increasing number of areas, the energy consumption of digital technologies themselves is also rising. This can be countered by developing energy-efficient devices and technologies.
Fraunhofer EMFT can build on expertise from previous projects, such as extremely energy-efficient tracking, sensor and communication systems from the Fraunhofer lead project "Towards Zero-Power Electronics". In cooperation with other Fraunhofer institutes, researchers are also working on a process chain for the interdisciplinary co-design of digital electro-optical transceivers with reduced energy consumption and high integration density. In the future, energy-efficient reference designs will also be made available to partners and industrial customers in the form of a database, and at the same time will be continuously adapted to the latest state of research.
In order to support the longest possible service life for electronic components, researchers at Fraunhofer EMFT are also developing concepts to take account of the reparability of a product as early as the development stage. In addition to this, new approaches are being developed in the area of packaging technology to facilitate reparability such as modularization, detachable connections, repair soldering, integrated production of cables and connectors and the separability of substrate and components.